Neurofeedback therapy, a cutting-edge approach in the field of mind and medicine, has gained significant attention in recent years. This innovative treatment method harnesses the power of the brain’s neuroplasticity to address a wide range of neurological and psychological disorders. By providing real-time feedback on brain activity, neurofeedback therapy aims to train individuals to self-regulate their brain function and improve their overall well-being.
However, behind this intriguing concept lies a complex web of scientific principles and practical applications that continue to puzzle researchers and healthcare professionals alike. In this discussion, we will explore the science behind neurofeedback, its various applications, and the potential benefits it holds for individuals seeking alternative therapies for their conditions.
Prepare to embark on a journey into the fascinating world of neurofeedback therapy, where the mind and medicine converge in unprecedented ways.
Understanding Neurofeedback Therapy
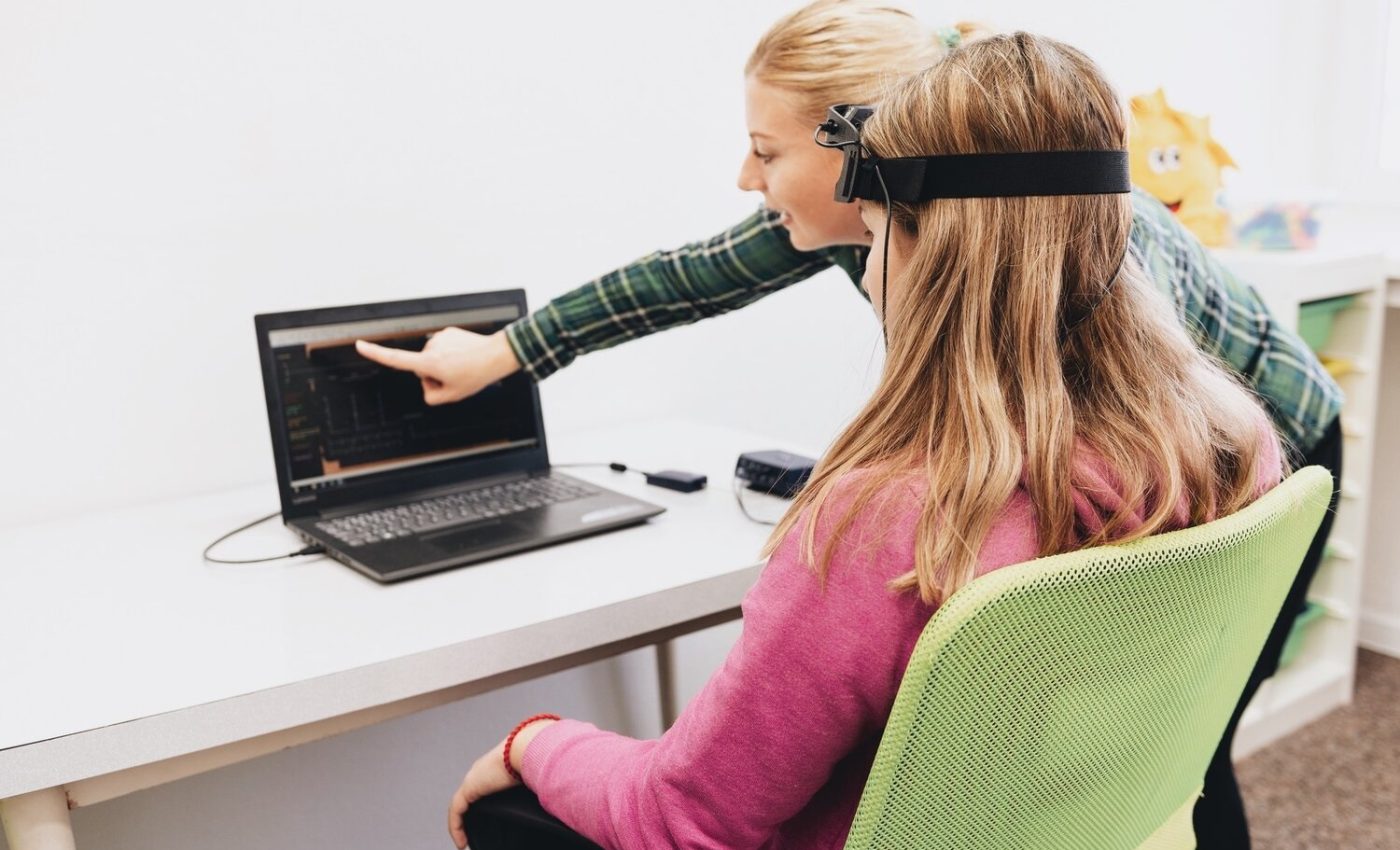
Neurofeedback therapy is a research-oriented approach that uses advanced technology to provide individuals with a better understanding of their brain activity and train them to regulate it effectively.
This therapy involves neurofeedback techniques, which aim to enhance self-regulation of brain functions. Neurofeedback training involves the use of specialized equipment to measure brainwave activity, such as electroencephalography (EEG).
By providing real-time feedback on brain activity, individuals can learn to recognize and modify their brainwave patterns. This training enables individuals to self-regulate their brain activity and achieve desired cognitive and emotional states.
Neurofeedback therapy has shown promising results in treating a range of conditions, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders.
The Science Behind Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback therapy is grounded in the science of brainwave activity and its relationship to cognitive and emotional functioning. Neurofeedback research has shown that specific patterns of brainwaves, such as alpha, beta, delta, and theta, are associated with different states of consciousness and mental processes. By utilizing neurofeedback techniques, therapists are able to monitor and measure these brainwave patterns in real-time, providing individuals with valuable information about their brain activity.
Neurofeedback research has demonstrated that individuals can learn to self-regulate their brainwaves through neurofeedback training. This training involves presenting individuals with visual or auditory feedback based on their brainwave activity, allowing them to learn how to modulate their brainwaves towards more desirable patterns. Over time, this can lead to improved cognitive and emotional functioning.
Neurofeedback techniques have been applied to a wide range of conditions, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and substance abuse. The scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of neurofeedback therapy continues to grow, making it a promising avenue for improving mental health and well-being.
Applications of Neurofeedback Therapy
The application of neurofeedback therapy spans a wide range of mental health conditions and has demonstrated promising results in improving cognitive and emotional functioning.
Clinical uses of neurofeedback therapy include treating attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and substance abuse disorders. Research findings suggest that neurofeedback therapy may be an effective alternative or adjunctive treatment for these conditions.
For example, studies have shown that neurofeedback therapy can lead to significant improvements in attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity in individuals with ADHD. Furthermore, research has also indicated that neurofeedback therapy may reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, enhance emotional regulation, and improve sleep quality.
These findings support the potential of neurofeedback therapy as a valuable treatment option for various mental health conditions, providing individuals with a non-invasive and drug-free intervention to improve their cognitive and emotional well-being.
Benefits and Effectiveness of Neurofeedback
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy and potential benefits of utilizing neurofeedback therapy as a non-invasive and drug-free approach for improving cognitive and emotional functioning in individuals with various mental health conditions.
Neurofeedback research has shown promising results in treating conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and substance abuse.
Neurofeedback training involves providing real-time feedback on brainwave activity to help individuals learn to self-regulate their brain function.
By training specific brainwave patterns, neurofeedback therapy aims to enhance attention, reduce impulsivity, regulate emotions, and promote overall well-being.
The effectiveness of neurofeedback is attributed to its ability to promote neuroplasticity, which refers to the brain’s capacity to reorganize and adapt its structure and function.
These findings highlight the potential of neurofeedback therapy as a valuable treatment option for mental health conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, neurofeedback therapy is a scientifically grounded approach that utilizes advanced technology to measure and train brain activity.
Its applications span across various fields, including mental health, performance enhancement, and rehabilitation.
Neurofeedback therapy has shown promising results in improving cognitive function, reducing symptoms of various neurological and psychiatric disorders, and enhancing overall well-being.
The effectiveness of this therapy is supported by a growing body of research, making it a valuable tool in the field of mind and medicine.