Mold exposure can have detrimental effects on our health, ranging from mild allergic reactions to severe respiratory issues. As the awareness about the potential dangers of mold grows, so does the need for accurate methods of detection.
While visual inspections and air quality tests are commonly used, blood tests have emerged as a promising tool in identifying mold-related health concerns. But how exactly do these tests work and what role do they play in detecting mold?
In this discussion, we will explore the science behind mold-related blood tests, the different types available, and how to interpret the results. Understanding the significance of blood tests in detecting mold exposure is essential for both individuals seeking answers and professionals working in the field.
So, let us embark on this journey to unravel the role of blood tests in the detection of mold-related health issues.
Understanding Mold Exposure Symptoms
Understanding Mold Exposure Symptoms is crucial for identifying and addressing potential health risks associated with mold contamination. Mold exposure can have various symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the extent of exposure.
Common symptoms include:
– Nasal congestion
– Coughing
– Sneezing
– Wheezing
– Itchy or watery eyes
– Skin rashes
– Throat irritation
People with respiratory conditions, allergies, or weakened immune systems may experience more severe symptoms. Prolonged or repeated exposure to mold can lead to chronic respiratory issues, such as asthma or bronchitis. Additionally, mold exposure has been linked to other health problems, including allergic reactions, sinusitis, and even neurological symptoms.
To prevent mold exposure, it is important to address any moisture issues in the home, such as leaks or high humidity. Regular cleaning and proper ventilation can also help reduce the risk of mold growth.
The Science Behind Mold-Related Blood Tests
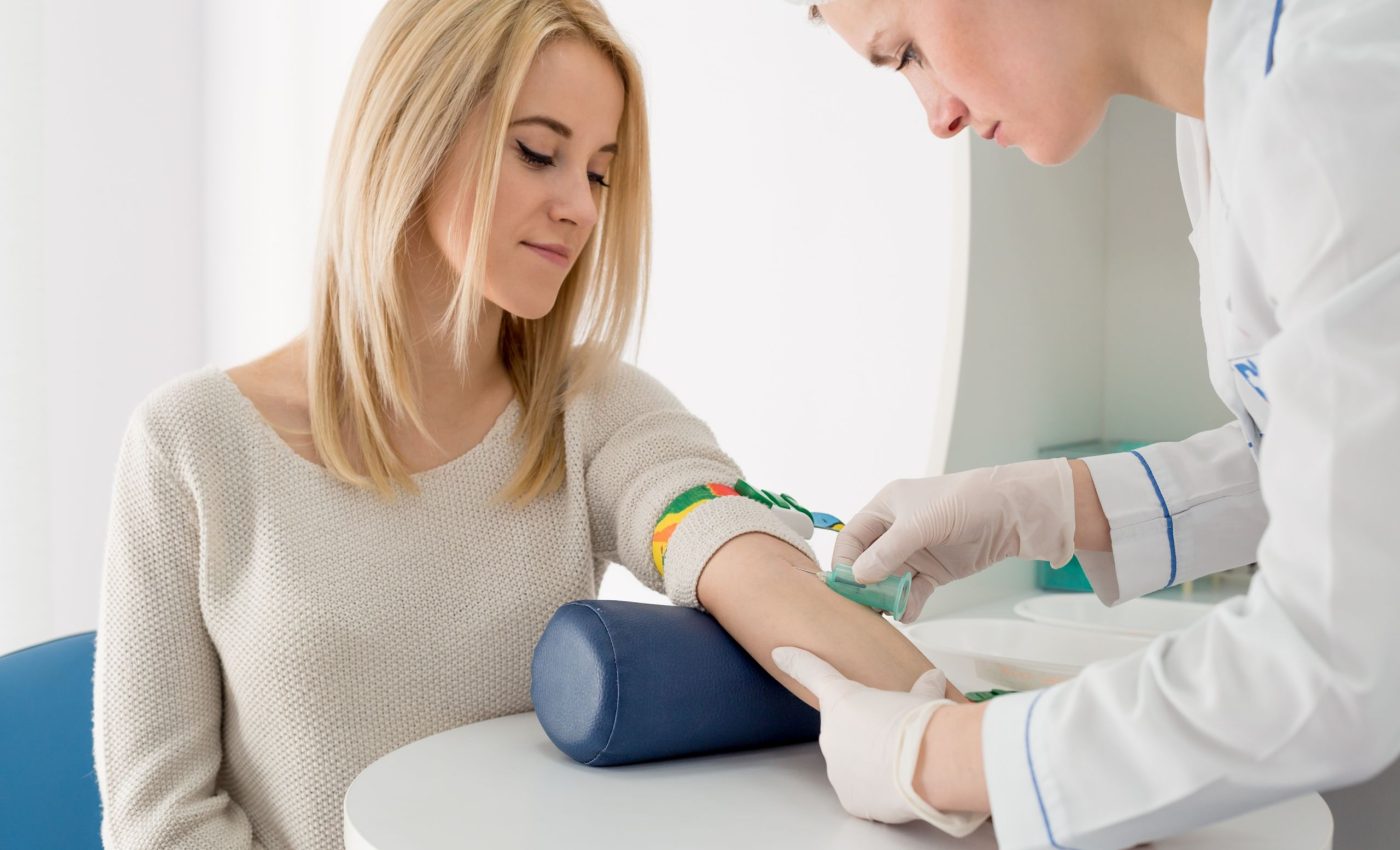
Mold-related blood tests provide valuable insights into an individual’s immune response and can help determine if there is a direct correlation between mold exposure and specific health issues. These tests are based on the science of immunology and the body’s immune system’s response to mold exposure.
Here are some key points to understand about the science behind mold-related blood tests:
– Mold-related blood tests measure specific antibodies in the blood that are produced when the immune system reacts to mold exposure.
– These tests can help identify if a person has been exposed to mold and if their immune system has mounted a response against it.
– Blood tests can also help determine the severity of the immune response and provide information about the specific types of mold to which an individual may be sensitive.
– These tests can be useful in identifying mold-related health risks and guiding appropriate treatment options.
– Additionally, blood tests can help evaluate the effectiveness of mold remediation methods by monitoring changes in antibody levels over time.
Understanding the science behind mold-related blood tests can help individuals and healthcare professionals make informed decisions about mold exposure and its potential impact on health.
Types of Blood Tests for Mold Detection
There are different types of blood tests available for the detection of mold exposure. These tests can help determine if an individual has been exposed to mold and if there is an ongoing mold-related health issue.
One type of blood test commonly used is the IgE antibody test. This test measures the levels of specific antibodies in the blood that are produced in response to mold allergens.
Another type of blood test is the mycotoxin test, which looks for the presence of mycotoxins, toxic substances produced by molds, in the blood.
Both of these tests have their own limitations, and it is important to note that blood test accuracy can vary. However, early detection of mold exposure through these blood tests can provide several benefits, including prompt treatment, prevention of further health complications, and identification of the source of mold contamination.
Interpreting Blood Test Results for Mold Exposure
To properly interpret blood test results for mold exposure, it is crucial to understand the significance of the specific antibodies or mycotoxins detected and their correlation to potential health implications.
Interpreting blood test accuracy can provide valuable information about an individual’s exposure to mold and the associated health risks. Here are five key points to consider when interpreting blood test results for mold exposure:
– **Identification of specific antibodies or mycotoxins**: The presence of specific antibodies or mycotoxins indicates exposure to mold and helps determine the type and severity of the exposure.
– **Reference ranges**: Comparing the levels of antibodies or mycotoxins detected to established reference ranges can provide insight into the significance of the exposure.
– **Symptoms correlation**: Assessing the individual’s symptoms in relation to the blood test results can help determine the potential health risks associated with mold exposure.
– **Timeframe of exposure**: Understanding the timing of the exposure can aid in interpreting the blood test results and identifying any potential chronic or acute health effects.
– **Consultation with a healthcare professional**: Interpreting blood test results for mold exposure should be done in consultation with a healthcare professional who specializes in environmental medicine or toxicology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood tests play a crucial role in detecting mold exposure. These tests help in understanding the symptoms associated with mold exposure and provide scientific evidence for its detection.
There are different types of blood tests available for mold detection, and interpreting the results can provide valuable information about the level of mold exposure.
Objective and evidence-based approaches are essential in understanding the significance of blood tests in identifying mold-related health issues.